Last Updated on October 13, 2025
Virtual data rooms (VDRs) have become the standard platform for managing the due diligence process in mergers, acquisitions, and other high-stakes transactions. Acting as secure online repositories, they give only authorized users controlled document access to confidential documents such as contracts, financial records, and compliance reports.
Central to this oversight are audit trails, sometimes referred to as audit logs. These chronological, tamper-resistant records track every piece of user activity inside the data room. Whether it’s uploading sensitive documents, downloading financial statements, or reviewing relevant documents, each action is captured with a timestamp.
This article will examine how audit trails in virtual data rooms work, the challenges organizations face in managing audit trails, and best practices for turning them into a source of trust, accountability, and resilience.
What Is an Audit Trail in a Virtual Data Room (and How It Works)
An audit trail in a virtual data room is essentially a digital logbook. It records every piece of user activity, from logging in to viewing, downloading, or sharing confidential documents. These audit logs ensure organizations can see exactly who accessed which file, when, and what actions were taken. Unlike traditional data rooms, where monitoring was limited, modern secure virtual data rooms create detailed records automatically to maintain data integrity and accountability.
Here’s how audit trail functionality works step by step:
- Login and verification – Only authorized users gain entry, often protected with two factor authentication.
- Action taken – The user views, edits, downloads, or uploads sensitive documents.
- Log created – The system records details such as user ID, timestamp, and document name.
- Storage – Entries are stored in the secure online repository as audit trail data.
- Reporting – Administrators can export these detailed audit logs as compliance documentation or review them during security incidents.
By capturing this level of user activity tracking, audit trails turn a VDR into more than just a file-sharing tool. They provide visibility into how sensitive information is handled, help organizations ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and give early warning signs of potential data breaches or compromising data security during high-value financial transactions and the due diligence process.
Compliance and Regulatory Importance in Audit Trails
One of the biggest reasons organizations rely on audit trails in virtual data rooms is to meet regulatory requirements. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and legal teams all handle sensitive information that must be tracked for regulatory compliance. Without compliance audit trails, it becomes difficult to demonstrate compliance during reviews or investigations, which can lead to fines and reputational damage.
Many industries operate under strict rules that require detailed audit logs of user activity and document access:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Ensures accountability for how organizations access sensitive data and protect sensitive patient data.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Requires healthcare organizations to track access to sensitive patient data and safeguard confidential documents.
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): Mandates compliance documentation around financial reporting and financial records.
- FINRA and SOC 2: Focus on auditability, data security, and strong access controls in financial services.
By keeping complete audit trails, companies can provide regulators with exportable compliance documentation that proves who accessed relevant documents, when, and why. This not only helps pass regular security audits but also reduces the time and cost of the diligence process. In high-stakes environments like M&A or financial reporting, the ability to show a clear, tamper-proof log of activity is essential to ensuring regulatory compliance and avoiding penalties.
Security and Risk Management in Audit Trails
Audit trails in virtual data rooms are more than just compliance tools, they are also a cornerstone of data security. By recording every instance of user activity and document access, these logs help organizations prevent data breaches, reduce insider risks, and respond effectively to security incidents. Below are the key ways audit trails strengthen risk management in practice.
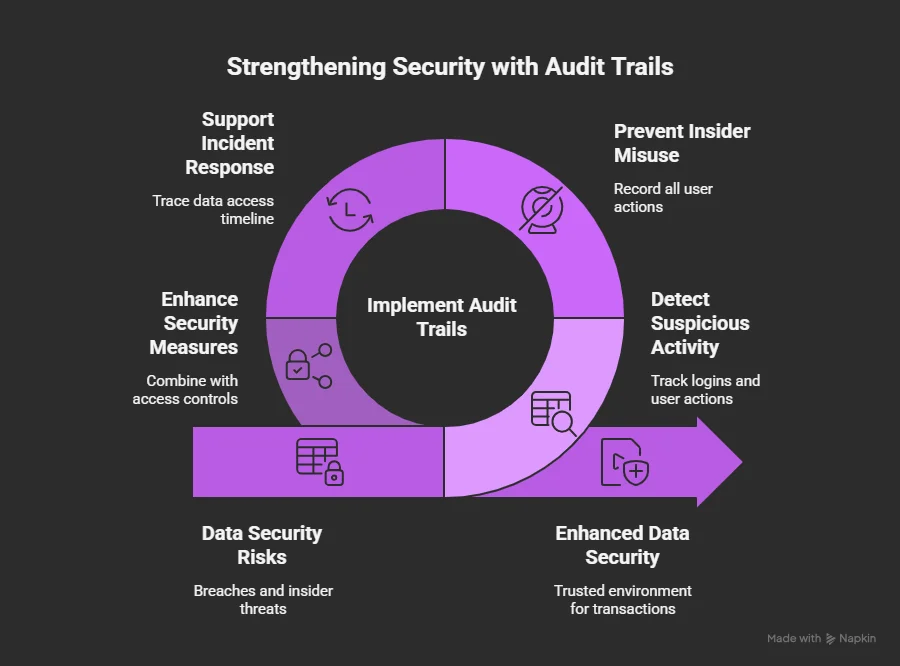
Detecting Suspicious Activity
Audit logs provide visibility into logins, IP addresses, and user actions. They highlight unusual patterns such as repeated failed logins, off-hour access to sensitive documents, or attempts to bulk download files. This real-time user activity tracking gives administrators early warning signs of potential security threats.
Preventing Insider Misuse
Insider misuse is one of the biggest risks for organizations handling confidential documents. With audit trail functionality, every action by authorized users is recorded. This accountability discourages misconduct and helps prevent data theft or accidental exposure of sensitive information.
Supporting Incident Response
When a security incident occurs, robust audit trails create a timeline of events. Investigators can trace how and when sensitive data was accessed, which relevant documents were compromised, and by whom. This clarity supports faster containment, effective risk management, and regulatory reporting.
Enhancing Security Measures
Combining audit trail systems with strong access controls, such as two factor authentication and regular security audits, ensures only authorized users can access sensitive data. These layered security measures transform secure virtual data rooms into trusted environments for critical financial transactions and the due diligence process.
Transparency and Business Value with Audit trails
Beyond compliance and security, audit trails in virtual data rooms also drive business value. They provide visibility into how confidential documents are used, build trust with external stakeholders, and streamline the due diligence process during major deals. This transparency turns audit logs into a competitive advantage, not just a technical feature.
Building Trust with Stakeholders
When organizations can show detailed audit logs of every user activity, it reassures investors, regulators, and partners that sensitive information is being handled responsibly. This level of transparency builds confidence, particularly during high-stakes financial transactions.
Streamlining the Due Diligence Process
In mergers, acquisitions, and fundraising, speed matters. Audit trail functionality captures every interaction with relevant documents, making it easy to track progress and verify that all parties had fair access. This reduces delays, cuts costs, and creates a more efficient diligence process compared to traditional data rooms.
Supporting Legal and Compliance Efforts
Clear audit trail data can serve as evidence in case of disputes after a deal closes. By showing exactly who accessed which sensitive documents and when, organizations can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and protect themselves legally. This transforms audit trails into both a compliance documentation tool and a safeguard for data integrity.
Challenges and Best Practices in Managing Audit Trails
While audit trails in virtual data rooms are essential for regulatory compliance and data security, they are not without limitations. Poorly designed audit trail systems or weak security measures can create gaps that undermine compliance efforts and even risk compromising data security. To maximize value, organizations need to recognize common obstacles and adopt proven strategies for managing audit trails effectively.
Common Challenges in Managing Audit Trails
Even with their benefits, audit trails in virtual data rooms are not without challenges. If not properly managed, they can introduce risks of their own:
- Over-reliance on logs without monitoring – Some organizations generate massive audit logs but rarely review them. Without active user activity tracking, suspicious patterns can go unnoticed.
- Data integrity and scalability issues – As the volume of sensitive documents grows, poorly configured audit trail systems may experience system failures or gaps that compromise data integrity.
- User privacy concerns – Tracking every detail of user activity can raise questions about privacy, particularly under frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Inconsistent policies – Failing to standardize log retention and review schedules can make it harder to provide compliance documentation during audits.
- Complexity of implementation – For smaller organizations, implementing audit trails with advanced security features may feel costly or overwhelming.
Best Practices for Strong Audit Trails
To overcome these hurdles, organizations should adopt a proactive approach to managing audit trails:
- Apply strong access controls – Use two factor authentication, robust access controls, and role-based permissions so that only authorized users can access sensitive data.
- Conduct regular reviews – Schedule regular security audits of audit trail data to spot anomalies early and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Secure backups and exports – Store detailed audit logs in a secure online repository, ensuring redundancy and availability for independent audits or regulatory checks.
- Train staff on compliance efforts – Employees should understand how audit trail functionality works and why it matters for protecting sensitive information and avoiding data breaches.
- Leverage advanced security features – Choose a virtual data room provider that offers monitoring alerts, anomaly detection, and reporting to strengthen risk management and prevent compromising data security.
Choosing the Right VDR for Audit Trails
Not all virtual data room providers offer the same level of audit trail functionality. To ensure your organization can meet regulatory requirements, protect sensitive data, and support the due diligence process, it’s important to evaluate VDRs based on their ability to deliver robust audit trails and strong security features.
Must-Have Compliance Features
A good provider should offer complete audit trails that can be exported as compliance documentation. Look for systems that allow you to generate reports for regulators, auditors, or external stakeholders without complex setup. This ensures you can easily demonstrate compliance during regular security audits or legal reviews.
Advanced Security Capabilities
Strong access controls are essential. Features like two factor authentication, IP or device restrictions, and secure access controls prevent unauthorized logins and keep sensitive documents safe. Providers that add advanced security features such as anomaly detection or alerting give administrators real-time visibility into user activity that could indicate security threats or potential data breaches.
Evaluating Cost vs. Value
When choosing a secure virtual data room, don’t focus only on price. The best providers combine enhanced security measures with reliable audit trail systems that protect confidential documents and ensure smooth transaction processes. A slightly higher cost may be worthwhile if the provider helps you avoid fines, reduce compliance efforts, and maintain data integrity during high-value financial transactions.
FAQ
What are the four different types of audit trails?
The four main types are:
User activity trails – track logins, logouts, and access attempts.
Document access trails – record actions like viewing, editing, or downloading files.
System audit trails – monitor configuration changes, permissions, and access controls.
Compliance audit trails – provide exportable reports to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
What is an audit trail in DB?
In databases, an audit trail is a record of changes made to the data. It logs inserts, updates, deletions, and user actions so administrators can ensure data integrity and recover from errors or system failures.
What is a data audit trail?
A data audit trail tracks the history of sensitive information, showing how, when, and by whom data was accessed or altered. It supports risk management, compliance efforts, and protection against data breaches.
What is an example of an audit trail?
An example is when an employee downloads financial records from a secure virtual data room. The audit trail data would log the user ID, timestamp, file name, and action (“download”), creating a detailed record for future review.
What is a compliance audit trail?
A compliance audit trail is a type of audit log specifically created to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. It provides complete audit trails and exportable compliance documentation that regulators, auditors, or independent audits can verify.
Conclusion
Audit trails in virtual data rooms are not just back-end logs, they are critical tools for regulatory compliance, data security, and transparency. By capturing every detail of user activity and document access, organizations can protect sensitive information, streamline the due diligence process, and provide regulators with clear compliance documentation. Choosing a virtual data room provider with robust audit trails ensures smoother transactions, stronger trust with stakeholders, and better preparedness for regular security audits.

Matthew Small is the Vice President of Strategic Sales and Alliances at SmartRoom, where he builds partnerships and leads strategic efforts to deliver cutting-edge virtual data room solutions for dealmakers. With a strong background in enterprise sales and channel development, Matthew is passionate about unlocking new growth opportunities and helping clients navigate complex transactions with greater speed, security, and confidence.


